Article source: TheBund on the Bund
The Paris Ladies’ Ball, where the world’s famous ladies broke their heads.
Three China girls were selected this year.
Not only beauty.
Their brains and talents are more outstanding.
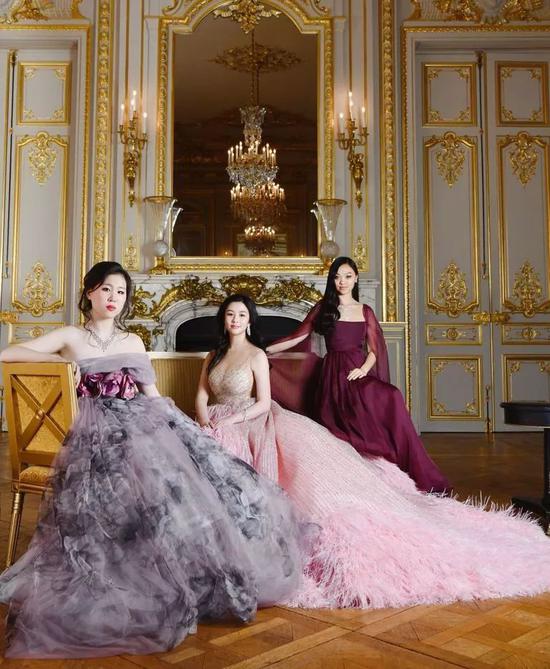
Not long ago, three girls from China made their appearance at the 25th Le Bal des Débutantes.
They are Shen Yue, the eldest daughter of Shen Jiawei, president of Chingmy Yau and Hongkong I T Group.
Jane Li, the eldest daughter of famous movie stars Jet Li and Nina Li Chi.
And Liao Minchong, the daughter of China’s famous baritone singer Liao Changyong.
The Paris Celebrity Ball can be said to be the most prestigious social admission ticket for the upper class. It was founded by a Frenchman, Ms. Ophélie Renouard, and only the top celebrities in the world can be invited.
Only the wealth of the family can not be favored by the organizing Committee. Girls must have their own talents, connotations and accomplishments, or be enthusiastic about public welfare undertakings.
Trump’s two daughters, despite their prominent family background, were repeatedly rejected by the organizing Committee.
The three China girls selected this year are all "the second generation of stars". Their parents have accumulated fame and wealth, and they have enough economic strength to give girls a good education and let them go their own way.
Today, let’s get to know these three "second generation" celebrities with both talent and brains.
01
Sweet and clever: Shen Yue
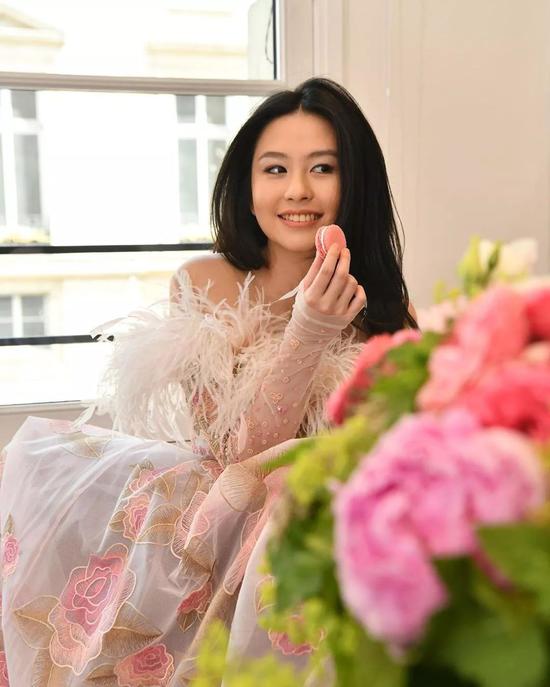
With Chingmy Yau, the mother of the goddess star, Shen Yue’s popularity can be said to be the highest among the three China girls this year. Dad, as the president of I.T. Group, need not say much about her fashion resources.
When Shen Yue was still in middle school, she was photographed when she attended Ku Kui Kei’s wedding with her mother Chingmy Yau, and was praised as "the most beautiful second generation" by the Hong Kong media. It was also rumored that she would enter the entertainment circle and take over the golden age of her mother.
However, these remarks were quickly refuted by Chingmy Yau, who said that she didn’t want her daughter to enter the entertainment circle. Now she still focuses on her studies and doesn’t want her to grow up surrounded by the media.
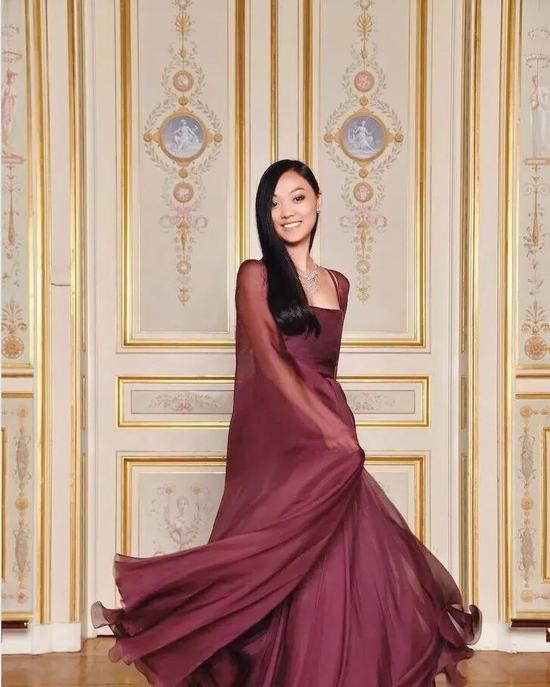
When Shen Yue was dressed in red, she could vaguely see the shadow of her mother, Chingmy Yau, dressed in red in Gambling God 2 when she was young. She also laughed off the comparison between her and her mother in the media, and said that her mother was the most beautiful in her heart, and no one could compare with her.
Being a "second generation of stars" since childhood, Shen Yue said that he had to learn to avoid the paparazzi cameras since childhood, so he was afraid to go out with his friends because he didn’t want to be photographed. She also revealed in an interview that when she was a child, she wanted to go to South Korea to form a women’s group, but now she has no such idea at all.
Before the dance began, she frequently posted her own fitting photos on Instagram and took a sweet and lovely route as a whole.
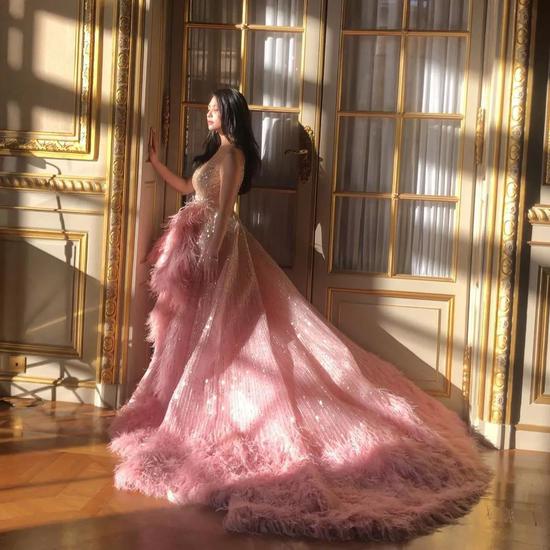
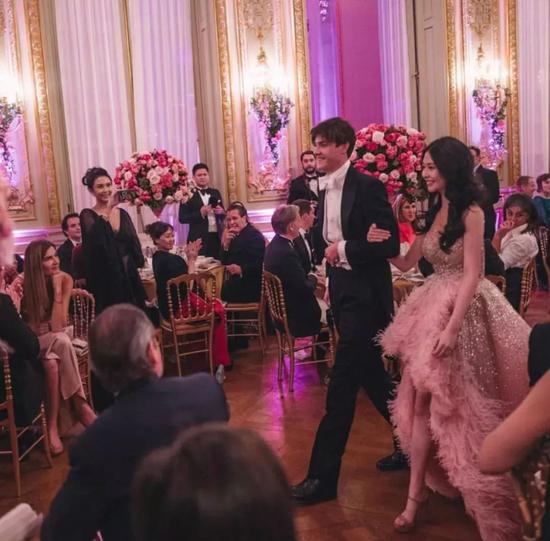
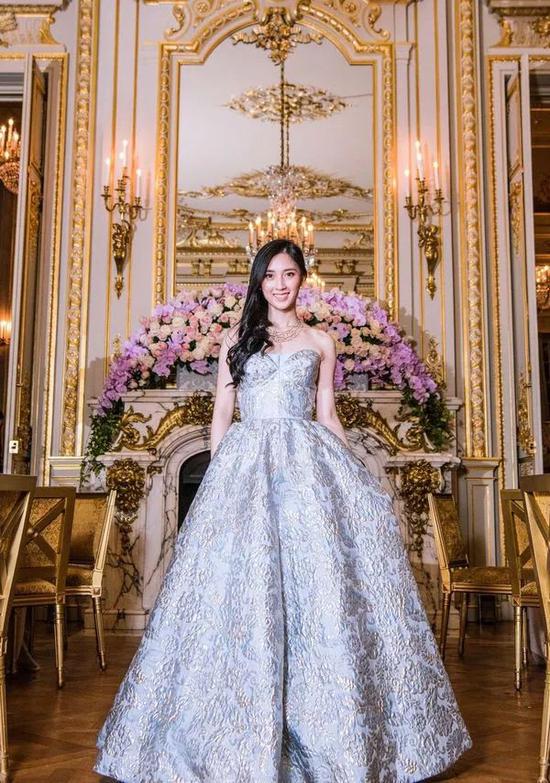
At the dance, she wore Georges Hobeika pink haute couture dress and walked into the venue with British boyfriend Timon Greaves.
Timon Greaves also gave a deep kiss on one knee, which is the princess dream of many little girls.
Mother Chingmy Yau has been filming and recording the important moments of her daughter’s life.
Shen Yue was very interested in fashion when he was a child. He read countless fashion magazines and loved to match clothes for himself and his sister. With this gift, father Shen Jiawei intends to let his daughter take over his own business, but he still insists that she must finish college.
Shen Yue, who is slim now, is studying in Vancouver’s UBC, majoring in innovative writing and psychology. In her spare time, she has walked the show for her own brand izzue and frequently appeared in the front row of the show.
Not long ago, she also appeared on the cover of the Hong Kong version of ELLE. Although she is still studying, she has already seen her ambition for the fashion circle.
Being a star in the spotlight or going behind the scenes to "inherit the family business", I believe Shen Yue will have the choice to follow her heart after graduation.
02
Learn to dominate the mind: Jane Li
Jane Li, who has a healthy wheat complexion, is the eldest daughter of Jet Li and Nina Li Chi. She is a proper schoolmaster at Harvard University. She once had dinner with Ma Yun with her father, and the dinner was natural and graceful.
Jane was born and raised abroad. Not only is her English comparable to her mother tongue, but Mr. and Mrs. Jet Li also ask her to speak Chinese fluently and remember her roots.
As a famous star in the Chinese world, Jet Li and his children’s lives are naturally concerned. He has always encouraged his daughter to do what she wants, but he also told her to be brave and not care about the comments of netizens.
On Jet Li’s 50th birthday, Jane painted 999 roses for him. He was particularly moved at that time, and this painting is still set in a frame for collection.
He said that he and Jane get along more like friends, and the role of "tiger mother" is played by Nina Li Chi. However, he also told his daughters that not touching drugs and not looking down on life, let alone getting pregnant before graduating from college, is the principle of a father’s life for his daughters.
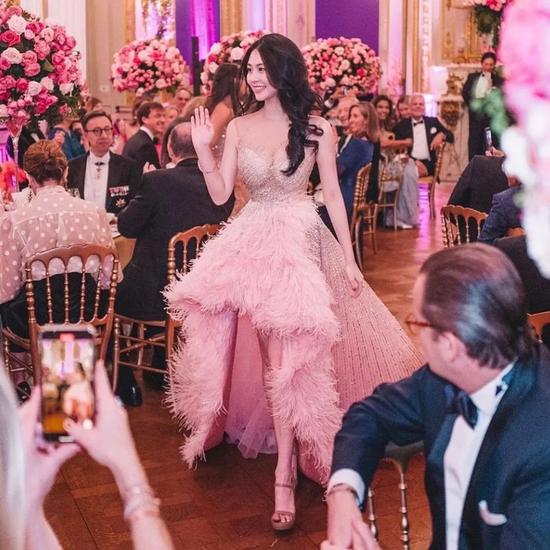
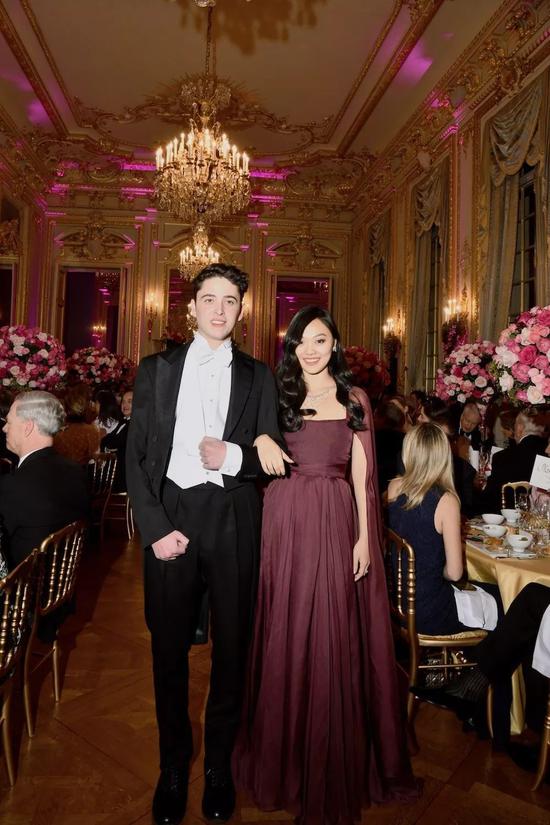
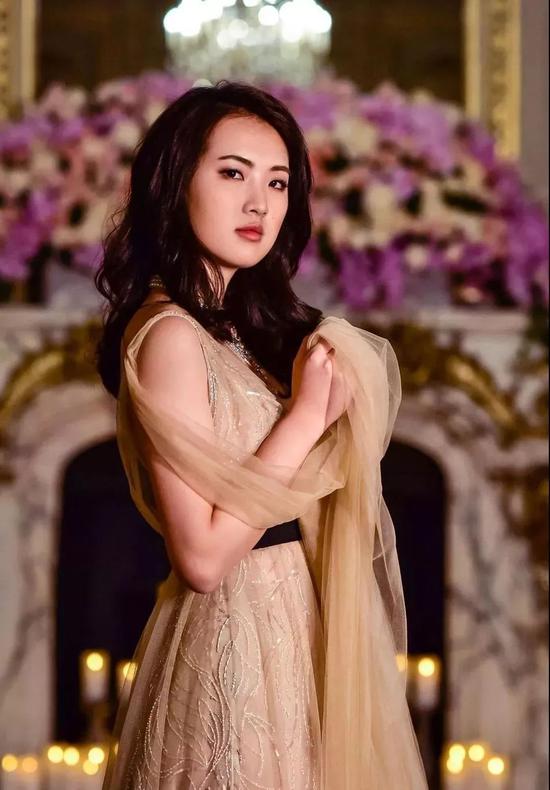
At the dance, Jane wore a Christian Dior high-definition dress, and the wine red made her look mysterious and noble.
In all the photos of celebrities, she still stands in position C.
At the dance scene, dad Jet Li was so happy that he kept taking pictures of his daughter and danced together.
Jane’s life with her father Jet Li is closely related to public welfare, which is a stepping stone for her to win the favor of the ladies’ ball.
After the Indonesian tsunami in 2004, Jet Li set up the One Foundation on Jane’s birthday, and the LOGO of the One Foundation was also selected by Jane, who was 4 years old at that time.
Before attending the celebrity dance, Jet Li and Ma Yun went to Africa to make a charity plan. Jane also took the initiative to ask her peers. She said that she had to go there to understand the actual situation before she could help others in a planned way.
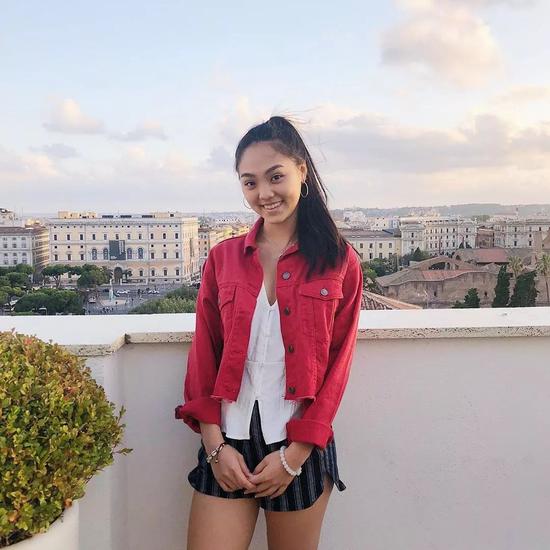
Looking through Jane’s Instagram, she looks like an ordinary international student, often posting photos with classmates and friends.
In the future, Jane said that she would help others as much as possible like her father and continue to carry forward charity. Bund Jun likes Jane’s confident and sunny smile best. Please keep smiling like this.
03
Touching voice: Liao Minchong
Before this celebrity dance, you probably didn’t know Liao Minchong’s name, but you must have heard the song of her father, Liao Changyong, the "world’s first Chinese baritone". Since this year, Liao Changyong has also been the dean of the Shanghai Conservatory of Music.
From an early age, Liao Minchong showed his extraordinary musical talent. At the age of 10, he began to perform on CCTV with his father, and often "grabbed" his father’s limelight in activities.
When celebrating the 90th anniversary of the founding of the Party, Liao Changyong and Liao Minchong sang "Sing a Folk Song for the Party" with their father and daughter, which surprised the audience.
The family background of a musical family and the experience of performing frequently when she was young made Liao Minchong pay attention to the celebrity dance. Because her father was busy with work, she went to Paris with her mother.
Like many celebrity families, Liao Changyong and his wife want to live an ordinary life, but they have always protected their daughter well and kept her from doing anything other than going to school and singing.
Liao Minchong, who is still a bit childish, may be the girl who came to Paris in the cheapest outfit. Her mother said that what she usually wears most is sportswear bought online for tens of dollars. She thinks that clothes just cover her body, so there is no need to be so extravagant.
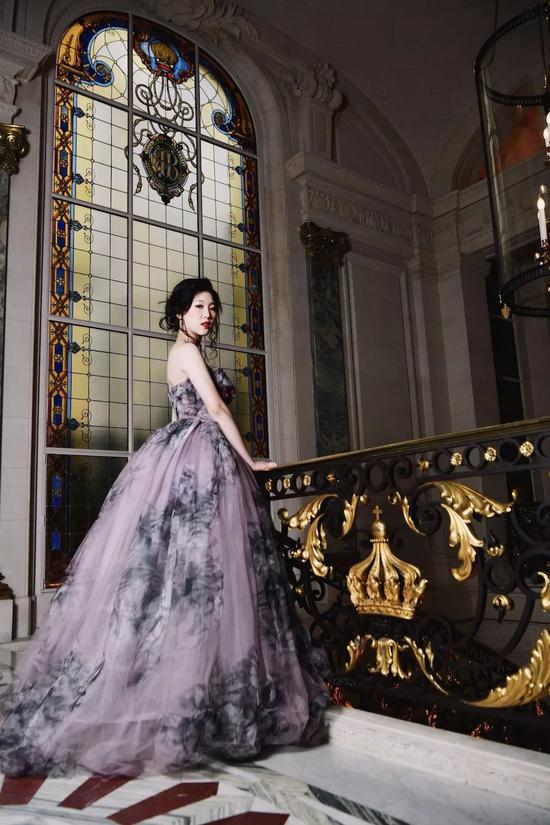
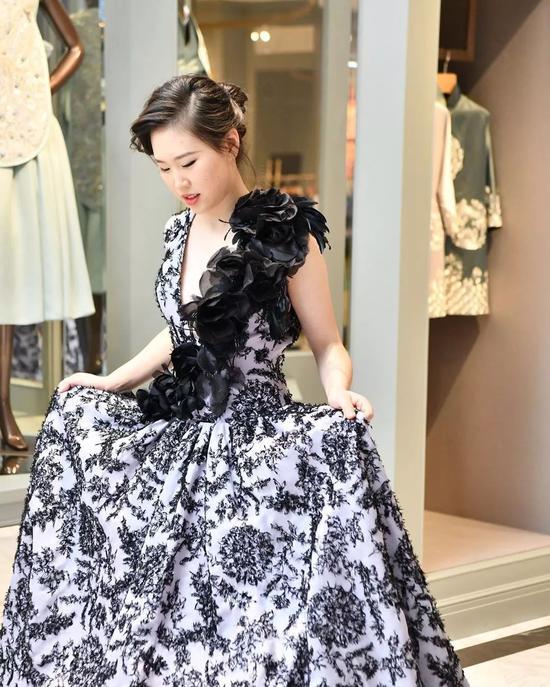
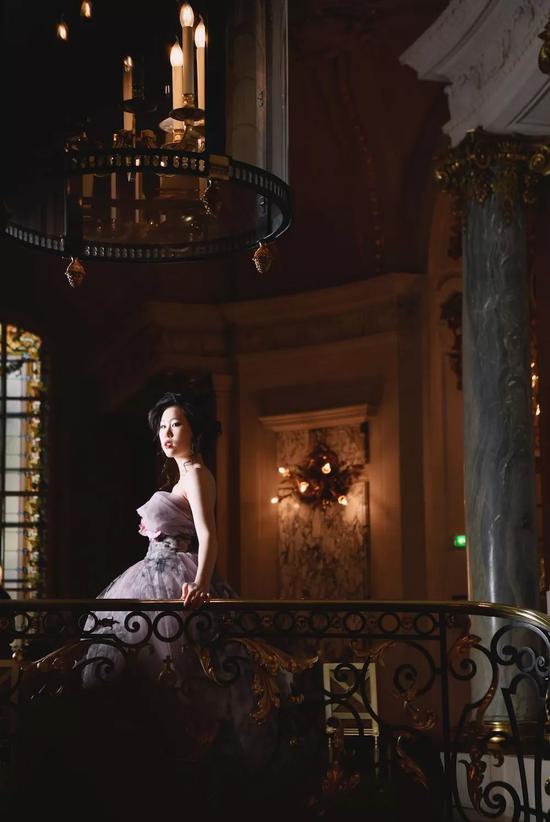
At the dance, she wore Guo Pei’s gray-purple high-cut dress and pretended to be serious with her partner for another second.
Liao Minchong is only 17 years old this year, the youngest of the three girls in China. She is still in a high school in Shanghai, and you can even meet her in the iapm shopping mall-just like meeting an ordinary high school student.
As of press time, there are only 209 fans on her Instagram, and a total of 5 pictures have been sent. Bund Jun only confirmed that this is not a counterfeiter by interacting with her message from Shen Yue.
Liao Minchong is still in high school. In the future, she is likely to use her expertise to study music, and she is looking forward to her future development.
In recent years, more and more China/Chinese celebrities have been invited to the Parisian Celebrity Ball.
Last year, I.M. Pei’s granddaughter Anna Pei attended the dance.
Yao Anna, daughter of Ren Zhengfei, president of Huawei Group.
Angel Lee, daughter of Li Zhikang, general manager of PCG Group in Hong Kong.
These Chinese girls are entrepreneurs or the "second generation of stars". They let the world see the brains and talents of the younger generation of women in China, and they also tell the world that although they have a prominent family background and outstanding appearance, good resources and education give them a smart and sexy mind, which others can never imitate.
We can’t help but look forward to it. Which China celebrities will attend this dance next year?